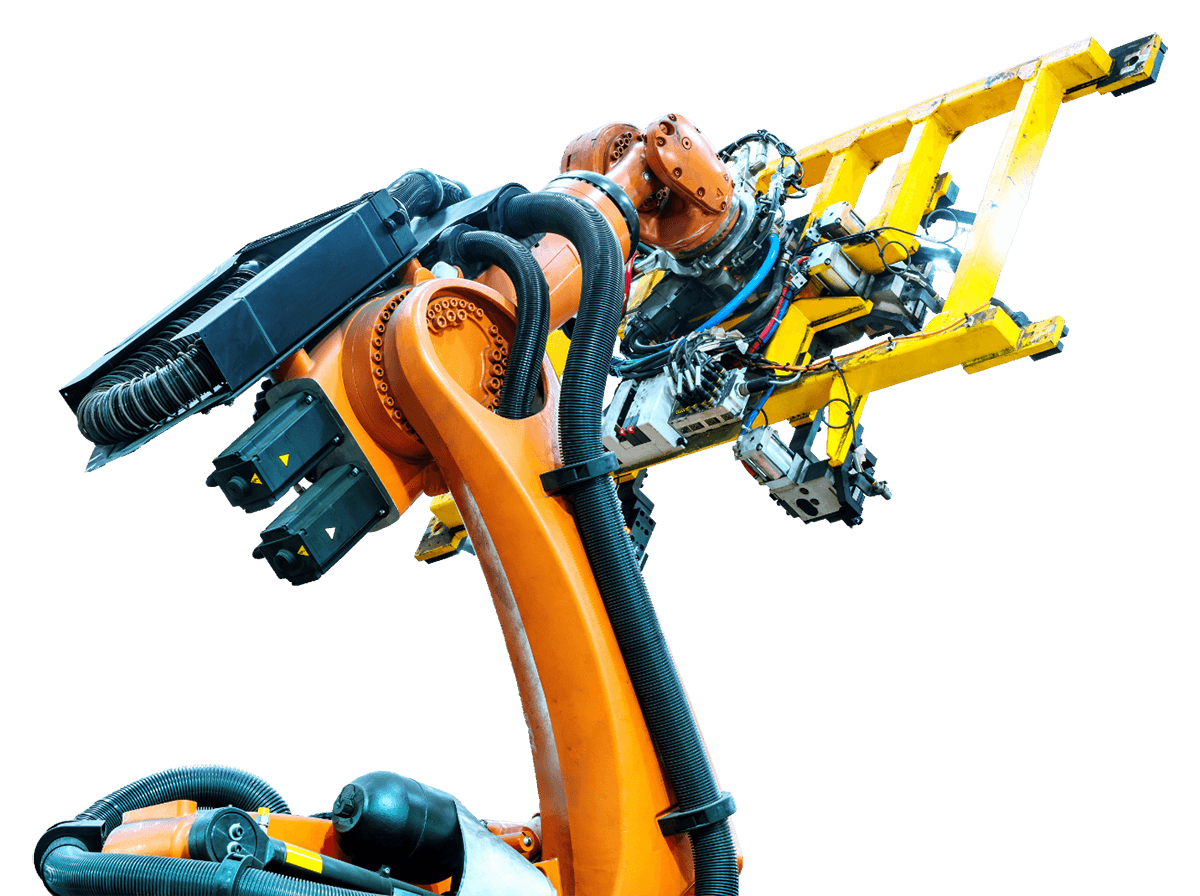
PICK AND PLACE
"Pick and place" applications most often require efficiency, precision and reliability at high speeds of parts transport or assembly processes. The most frequently automated processes are:
\ assembly of workpieces / electronics components,
\ sorting products,
\ reorientation of workpieces on conveyors,
\ inspection and detection of damaged workpieces,
\ transfer of workpieces between machines,
\ searching and unloading elements from collective packaging,
\ packaging products,
\ packing and repacking so-called mixes.

"pick and place" application:
In product transfer applications, many types of robots are used. The selection of the right solution is associated with the requirements of the application and the type of workpieces to be moved. In applications with high dynamics and small workpieces, the most commonly used robots are:
\ delta,
\ scara,
\ articulated robots (anthropomorphic).
In applications for transferring heavier parts, there are usually used articulated robots in the standard version or possibly in the cooperating version.
Cooperating robots have movement dynamics limitations appropriate to the size and shape of the workpiece they operate, so as to meet the standards for cooperation with human.
When transferring larger parts with appropriate dynamics, there are solutions of classic articulated robots to be used.

in intra-logistics systems:
“Pick and place” applications are often used in intra-logistics systems or as a supplement to in-house transport.
Robots added to the conveyor system, using appropriate automation systems, are able to synchronize their movements with the speed of products transport, enabling sorting or reorientation in flight.
Properly selected vision systems can be the heart of inspection systems directly on conveyors. They control e.g. levels of filling, material defects or losses in details. Using a robot, we can remove defective items from the production line. Such activities significantly simplify and speed up quality control processes as well as save costs of equipment maintenance and transport of workpieces to quality departments and then to subsequent production stages.
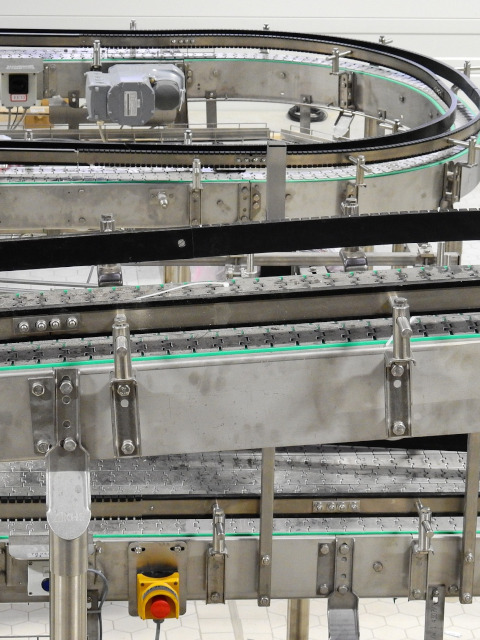

It is possible to use then dedicated manipulators for simple trajectories or an industrial robot, where maneuvering involves a complete change of orientation or is carried out in significantly limited spaces.
Dedicated grippers and materials ensure the opportunity of contact with food, a steady grip and the possibility of leaving no marks on the surface, on which the working element of the gripper worked.
Such features are an undoubted advantage for the food, pharmaceutical and many other industries, where there is a possibility of product pollution or contamination with traditional handling.
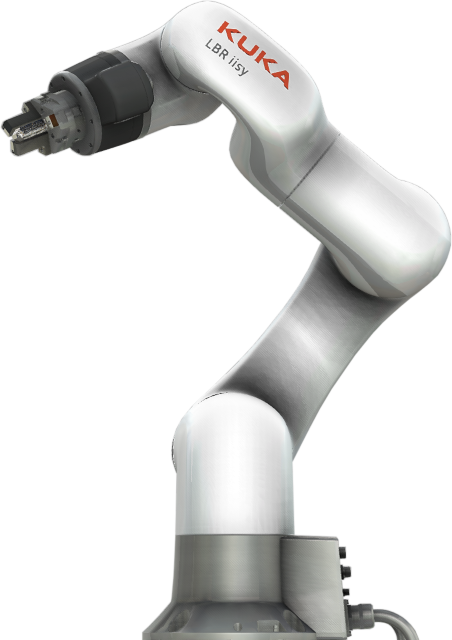
cooperating robot:
Cooperating robot or “Cobot”, is new solution in the world of automation, although it’s becoming more and more popular.
Cobots are usually robots with articulated construction, equipped with additional sensors and modified software. This design allows for safe interaction with the environment and work without additional security systems in direct proximity to people.
Programming cobot, at least in basic applications, is also simplified. Arrangement of buttons on the robot's bunch or an additionally added remote control allows to program arm movement by moving the head from point to point. Grippers in such constructions have similar systems, allowing for quick programming of the head operation at a certain point.
Cobot will work, among others, where we have to carry out the assembly procedure, complicated from the point of view of repeatability and movement. Similarly monotonous are processes in which the presence of an employee at certain stages is still indispensable.
However, cobots have some limitations, taking into consideration the safety of work with human. According to standards, the size and sometimes also the shape of the object may be a limitation, directly affecting the permissible dynamics of work, so that no serious collision or injury occurs in contact with the human body.
Modern autonomous systems, powered with built-in energy sources, carry out the processes of packaging, product completion, and then transport workpieces between stages of production or processing stations.
The mobile robots themselves in the form of mobile trolleys can be used as warehouse trolleys, systems for supplying components to production stations or systems for transporting parts between CNC centers and automatic loading and unloading of part stacks.
Construction solutions of the linear units allow for maneuvering with workpieces in much smaller spaces with greater precision than in the case of traditional systems based on forklifts, and thanks to sets of sensors and scanners, they provide a much higher level of security.